In 2025, fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) has moved from theoretical promise to practical engine for confidential smart contracts. While blockchain’s transparency is foundational for trust, it’s also a double-edged sword: every transaction and contract state is visible to all participants. This visibility, though essential for auditability, poses critical privacy challenges for enterprises, DeFi protocols, and users handling sensitive data. FHE solves this by enabling computations on encrypted inputs, so even smart contract logic can operate without ever exposing the underlying data.
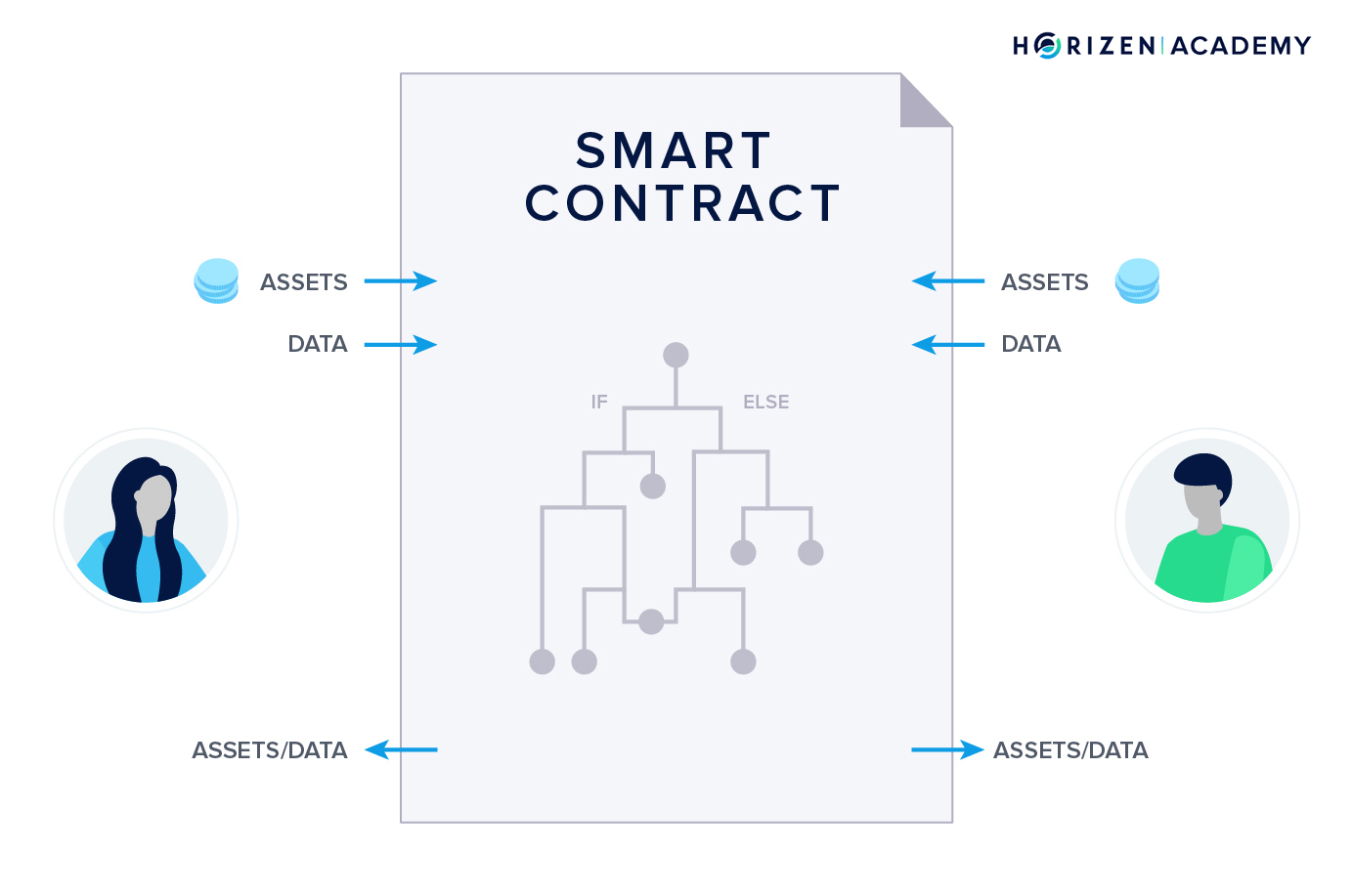
The Rise of FHE Coprocessors: Zama and the fhEVM Revolution
Historically, privacy solutions like zero-knowledge proofs or multi-party computation required deep cryptographic knowledge and often introduced trade-offs in usability or composability. In contrast, Zama’s fhEVM Coprocessor has redefined developer experience. By allowing Solidity smart contracts to process encrypted values natively on any EVM-compatible chain (Ethereum, Base, Polygon), Zama has made private dApp development accessible without requiring developers to become cryptographers.
This breakthrough has catalyzed a wave of confidential applications in sectors ranging from DeFi to real-world asset tokenization. For instance, confidential lending protocols can now verify collateral and execute liquidations while keeping user positions entirely private from both competitors and the public ledger.
Zama Confidential Blockchain Protocol: End-to-End Privacy Across Chains
The June 2025 launch of the Zama Confidential Blockchain Protocol marked a significant leap forward in blockchain privacy. This cross-chain protocol enables encrypted transaction inputs and persistent encrypted states across Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains. By leveraging FHE for computation at every stage, it preserves confidentiality without sacrificing the composability that underpins open finance.
Developers can now build cross-chain applications where sensitive business logic, such as voting in DAOs or managing on-chain payroll, is never exposed even as it interacts with other protocols. The protocol’s architecture ensures that encrypted data flows seamlessly between chains while remaining fully auditable by authorized parties with decryption keys.
Industry Adoption: Confidential Tokens and Encrypted DeFi Protocols
The practical impact of FHE is perhaps most visible in the rapid adoption of confidential tokens. In partnership with OpenZeppelin, Zama introduced a standard interface akin to ERC20 but with encrypted balances and transaction values. This innovation addresses one of DeFi’s core weaknesses, exposed wallet balances, enabling institutions to participate in decentralized markets without revealing sensitive financial positions.
These confidential tokens are already being integrated into lending platforms, AMMs, and insurance pools where privacy was previously impossible without off-chain workarounds. As more protocols adopt these standards, expect a new class of encrypted DeFi protocols that combine composability with robust privacy guarantees.
Academic research has reinforced the trajectory of fully homomorphic encryption smart contracts by dissecting not only their cryptographic underpinnings but also their practical deployment. The 2025 “SoK: Fully-homomorphic encryption in smart contracts” paper highlights how FHE uniquely addresses privacy challenges endemic to transparent blockchains, allowing computation on encrypted data while retaining automation and decentralization. This approach is particularly relevant for sectors such as healthcare, supply chain, and finance, where data sensitivity is paramount.
Beyond Ethereum, new entrants like Fhenix have expanded the FHE landscape by integrating threshold FHE (TFHE) into Layer 2 rollups. Their architecture supports confidential execution on EVM chains, lowering both latency and cost barriers and opening the door to scalable private applications. These advances demonstrate that FHE’s utility is not confined to a single blockchain or protocol but is rapidly becoming an industry-wide standard for privacy-preserving computation.
Real-World Applications: From Private Voting to Encrypted Real World Assets
The impact of confidential smart contracts in 2025 is evident across diverse use cases:
Leading Use Cases of FHE-Powered Confidential Smart Contracts
-

Confidential DeFi Protocols: Platforms like Zama’s fhEVM Coprocessor and Fhenix enable decentralized finance (DeFi) applications to process trades, loans, and transactions directly on encrypted data, ensuring user balances and strategies remain private.
-

Private DAO Voting: With FHE, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) can conduct on-chain voting where individual ballots are encrypted, as demonstrated by Zama’s Confidential Blockchain Protocol, preserving voter privacy without sacrificing transparency or auditability.
-

Encrypted Payroll Management: FHE-powered smart contracts allow organizations to manage payroll on-chain while keeping salary data confidential. Solutions leveraging the fhEVM Coprocessor enable encrypted salary disbursements and private employee records.
-

Secure Real World Asset Tokenization: Confidential smart contracts, such as those using the Confidential Token standard by Zama and OpenZeppelin, facilitate the tokenization of real estate, equities, or commodities, ensuring asset ownership and transaction details remain private on public blockchains.
DAOs are leveraging FHE-powered voting mechanisms that ensure ballot secrecy without sacrificing verifiability or auditability. Enterprises are deploying encrypted payroll systems on-chain, allowing HR departments to automate salary disbursement without exposing employee compensation details publicly. Meanwhile, tokenization of real world assets, such as real estate or trade receivables, now benefits from encrypted ownership records and transaction histories that comply with regulatory privacy requirements.
This proliferation of use cases is driving a shift in how users and institutions perceive blockchain privacy. Rather than being a niche feature reserved for specialized applications, confidentiality powered by FHE is fast becoming a baseline expectation for modern decentralized infrastructure.
Challenges Ahead: Performance, UX, and Regulatory Alignment
Despite these breakthroughs, the journey toward ubiquitous confidential smart contracts is not without obstacles. The computational overhead of FHE remains significant compared to traditional cryptography. While Zama’s fhEVM Coprocessor and related innovations have made great strides in optimizing performance for mainstream use, further research is required to reach parity with plaintext execution speeds.
User experience also presents hurdles: key management for decryption must be seamless yet secure; developers need robust tooling and documentation; end-users require clear assurances about what data remains private under various threat models. Moreover, as confidential DeFi protocols gain traction, regulators will scrutinize how privacy interacts with anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), and tax compliance frameworks.
The Road Ahead for Confidential Smart Contracts
Looking forward, the interplay between innovation and adoption will define the next chapter for fully homomorphic encryption smart contracts. As more projects integrate FHE coprocessors and cross-chain confidentiality protocols mature, we will see a new generation of applications that treat privacy as a default rather than an afterthought.
For developers seeking practical guidance on implementing these technologies in EVM environments or exploring deeper technical analysis of usability trade-offs in FHE-powered dApps, our dedicated resources offer actionable insights:
- How Fully Homomorphic Encryption Enables Confidential Smart Contracts on Any Blockchain
- How Fully Homomorphic Encryption Enables Usable Privacy in Smart Contracts
- How Fully Homomorphic Encryption Enables Truly Confidential Smart Contracts on Public Blockchains
The momentum behind confidential smart contracts 2025 signals a paradigm shift where confidentiality coexists with composability – unlocking new markets for encrypted DeFi protocols, private real world assets blockchain solutions, and beyond. As technical barriers fall away and industry standards solidify, expect privacy-preserving computation to become as fundamental to Web3 as consensus itself.






