Privacy has long been the missing link in Ethereum’s smart contract ecosystem. While the blockchain’s transparency is a pillar of trust, it’s also a liability for sensitive use cases like private DeFi, confidential voting, or secure identity management. The arrival of fully homomorphic encryption smart contracts is shifting this paradigm, making confidential computation on Ethereum not just possible, but practical.
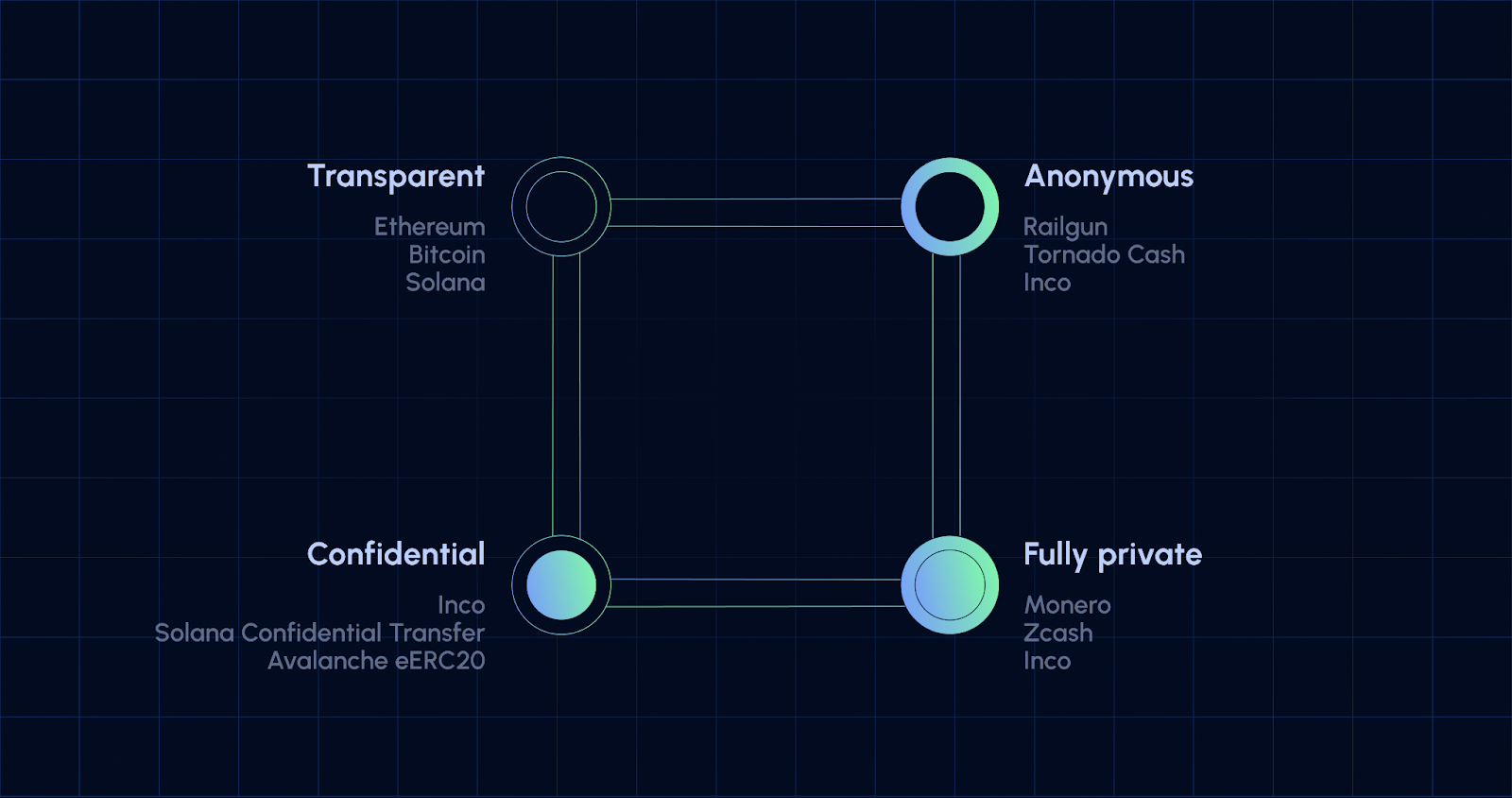
What Is Fully Homomorphic Encryption and Why Does It Matter?
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) allows computations to occur directly on encrypted data. Imagine being able to add, multiply, or process numbers without ever seeing their actual values. This isn’t just theoretical: FHE is rapidly moving from the academic world to real-world applications, especially in blockchain where on-chain data privacy is critical.
Traditional Ethereum smart contracts are transparent by design. Every transaction, every variable, and every contract state is visible to anyone. While this ensures verifiability, it’s a dealbreaker for enterprises and privacy-conscious users. FHE flips the script: it lets smart contracts operate on encrypted inputs and maintain encrypted states, so sensitive details never leak on-chain.
“FHE is in a unique position to address blockchain-related problems such as Miner Extractable Value (MEV), which is associated with transaction front-running and privacy leaks. ” – SoK: Fully-homomorphic encryption in smart contracts
How FHE Powers Confidential Smart Contracts on Ethereum
Recent breakthroughs have made FHE viable for blockchain-scale computations. The most prominent implementation is Zama’s fhEVM, which brings FHE to EVM-compatible chains. Developers can now write smart contracts in Solidity that process encrypted data end-to-end, without needing deep cryptography expertise.
Here’s how it works in practice:
Top Benefits & Use Cases of FHE-Enabled Smart Contracts on Ethereum
-

Confidential Financial Transactions: FHE-enabled contracts, like those built with Zama’s fhEVM, allow users to transact securely on Ethereum without exposing transaction details, balances, or sensitive business logic.
-

Private Voting Systems: Solutions such as Fhenix’s FHE Rollup enable fully private on-chain voting, ensuring ballots remain confidential while maintaining verifiable results.
-

Secure Identity Management: FHE smart contracts keep user identities and credentials encrypted throughout processing, enabling decentralized identity systems that protect personal data from public exposure.
-

Protection Against MEV (Miner Extractable Value): By encrypting transaction data, FHE-based contracts prevent front-running and other MEV attacks, enhancing fairness and security for users and dApps.
-

Composability with Privacy: Platforms like fhEVM allow developers to build confidential DeFi protocols that interoperate seamlessly with other smart contracts, unlocking new privacy-preserving financial applications.
The fhEVM acts as a confidential computation layer for Ethereum. It’s EVM-compatible, so existing developer tools and workflows remain intact. Smart contracts can accept encrypted inputs, perform computation in the encrypted domain, and output encrypted results. Only parties with the right decryption keys can reveal the underlying data.
Another notable project is Fhenix’s FHE Rollup, which combines the scalability of optimistic rollups with FHE’s privacy guarantees. This approach unlocks confidential voting, private games, and secure financial contracts at scale.
FHE vs. Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Complementary, Not Competing
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) have dominated the privacy conversation in blockchain for years, allowing users to prove statements without revealing underlying data. But ZKPs often require complex setups and are limited to specific types of proofs. FHEVM Ethereum privacy solutions, by contrast, enable general-purpose computation on encrypted data, supporting a wider range of confidential smart contracts.
Think of ZKPs as a way to verify that something is true without seeing the details, while FHE lets you actually compute with those details – all while they stay hidden. The two technologies are increasingly seen as complementary. In fact, projects like fhEVM are exploring ways to combine FHE with ZKPs and multi-party computation (MPC) for layered privacy.
Current State of FHEVM and What’s Next
The technology is still evolving, but Zama’s fhEVM and Fhenix’s FHE Rollup have already demonstrated functional confidential smart contracts on testnets. Solidity developers can use libraries like zama-ai/fhevm-solidity to start experimenting with encrypted computation, opening the door to private DeFi, on-chain encrypted computation, and more.
Momentum is building. With the first confidential lending protocols, private auctions, and encrypted on-chain games already prototyped, the next generation of confidential smart contracts blockchain use cases feels imminent. The developer experience is familiar, but the privacy guarantees are radically new. On fhEVM, inputs, states, and outputs remain encrypted, yet computations unfold seamlessly, no trusted third parties, no data leakage, and no compromise on composability.
“FHE is a game changer for DeFi privacy. Imagine a world where your collateral, bids, and votes are all confidential, but still verifiable on-chain. ” – Clara Jennings, Encrypted Smart Contracts
What’s more, FHE is uniquely positioned to neutralize front-running and MEV (Miner Extractable Value) attacks. Since transaction data stays encrypted until after block inclusion, malicious actors can’t exploit sensitive information in the mempool. This is a breakthrough for fair markets and user protection, especially as DeFi volumes surge.
Challenges and the Road to Mainnet
Of course, there are hurdles. FHE computations are more intensive than traditional EVM operations. Early implementations require specialized coprocessors or off-chain helpers to keep latency and gas costs manageable. But with ongoing research and hardware acceleration, these bottlenecks are shrinking fast. Projects like Zama and Fhenix are racing to optimize performance, aiming for mainnet deployments that feel as smooth as standard Ethereum contracts.
Developers and enterprises exploring private DeFi encrypted contracts can already experiment with testnet deployments, leveraging open-source libraries and comprehensive documentation. As the ecosystem matures, expect toolkits, SDKs, and standards to emerge, lowering the barrier even further for confidential dApp development.
Top Real-World Uses of FHE Smart Contracts
-
Confidential DeFi Transactions: Platforms like Zama’s fhEVM enable users to perform decentralized finance operations—such as swaps, lending, and portfolio management—while keeping transaction data and balances fully encrypted, protecting user privacy on public blockchains.
-

Private On-Chain Voting: Using Fhenix’s FHE Rollup, organizations and DAOs can conduct secure, transparent elections where individual votes remain encrypted, ensuring both verifiability and voter privacy.
-

Secure Identity Management: FHE-powered smart contracts allow users to prove credentials or attributes (like age or residency) without revealing sensitive personal data, enhancing privacy for KYC and access control on Ethereum.
-

Confidential Auctions & Bidding: With FHE-enabled contracts, participants can submit encrypted bids, ensuring that no party—including the contract operator—can see bid amounts until the auction closes, preventing front-running and collusion.
-

Private Gaming & Gambling: FHE smart contracts allow for fully encrypted in-game moves, bets, and outcomes, enabling fair and private on-chain gaming experiences where strategies and results are shielded from public view.
Security audits and formal verification remain critical. Even with encrypted computation, contract logic must be airtight to prevent subtle leaks or misuse of decryption keys. Collaborations with security leaders like OpenZeppelin signal that rigorous best practices are being integrated from day one (source).
Why FHEVM Ethereum Privacy Matters Now
The privacy revolution isn’t theoretical anymore. With fhEVM and FHE Rollups, Ethereum is on the cusp of supporting mainstream applications that demand both transparency and confidentiality. Think private payrolls, confidential DAO governance, on-chain insurance, and cross-border payments, all without sacrificing decentralization or composability. For enterprises, this means regulatory compliance and data protection. For users, it’s true financial privacy, on their terms.
As on-chain encrypted computation becomes practical, expect a wave of innovation across sectors: from healthcare data sharing to private NFT ownership and beyond. The synergy between FHE, ZKPs, and MPC will likely define the next decade of blockchain privacy architecture. The only question is: who will build the killer app?






