Confidential smart contracts are rapidly transforming the blockchain privacy landscape, especially for enterprises seeking to balance data confidentiality with regulatory mandates. As blockchains become more mainstream across finance, healthcare, and supply chain sectors, the demand for regulatory-compliant privacy solutions is intensifying. The challenge: how do you keep sensitive onchain data private while still providing auditability and transparency for compliance?

Privacy Meets Compliance: The New Standard for Enterprise Blockchain
Traditional public blockchains are designed for radical transparency. Every transaction is visible to all participants, which is great for trust but problematic for organizations subject to strict data protection laws or handling proprietary information. Confidential smart contracts bridge this gap by leveraging advanced cryptography and secure hardware to shield transaction details from the public while preserving the ability to selectively disclose information.
The latest advances are not just theoretical. Financial institutions and healthcare providers now use confidential contract protocols that combine Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs). These technologies empower organizations to prove compliance – such as AML or KYC checks – without exposing customer identities or transaction specifics onchain.
Key Benefits of Confidential Smart Contracts
-

Selective Data Disclosure for Compliance: Confidential smart contracts enable selective de-anonymization, allowing enterprises to reveal only necessary transaction details to regulators while keeping sensitive business data private. Protocols like SeDe exemplify this approach.
-
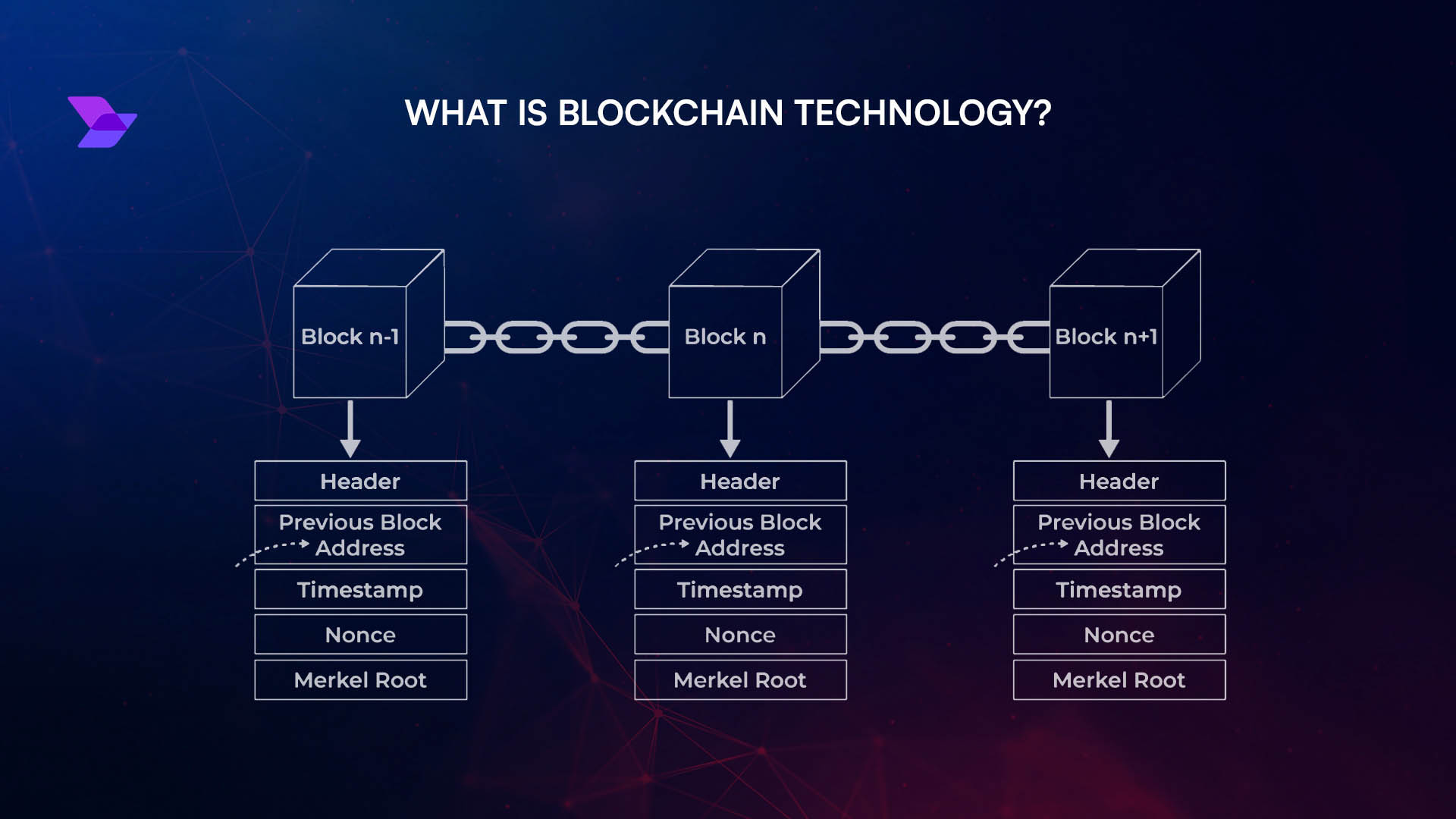
Privacy-Preserving Computation: By leveraging Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), smart contracts can process confidential data securely, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected even from blockchain node operators. IBM Blockchain uses TEEs for enterprise-grade privacy.
-
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) for Secure Validation: ZKPs allow contracts to prove the validity of transactions without exposing underlying data. This technology is widely adopted in privacy-focused blockchain solutions, such as Chainlink Blockchain Privacy Manager.
-

Immutable and Auditable Compliance Trails: Confidential smart contracts create tamper-proof audit trails that regulators can verify, supporting transparency and accountability without sacrificing privacy. This is crucial for industries like finance and healthcare.
-

Private Cross-Chain Transactions: Solutions such as Chainlink’s Blockchain Privacy Manager enable enterprises to conduct private transactions across multiple blockchain networks, minimizing on-chain data exposure while maintaining compliance.
How Confidential Smart Contracts Enable Regulatory-Compliant Privacy
The core innovation lies in selective disclosure. For example, protocols like SeDe allow authorized regulators to view specific transaction attributes without granting them access to the entire dataset (arxiv.org). This means companies can comply with legal requirements without risking a wholesale data leak.
Audit trails remain immutable and verifiable, but only reveal what’s necessary to satisfy auditors or regulators. This approach is already being adopted in cross-chain environments where privacy must be maintained even as assets move between networks (blog.chain.link). Secure oracles play a crucial role here by feeding only essential decision outputs into smart contracts – reducing unnecessary exposure while maintaining full regulatory traceability.
The Technology Stack: TEEs, ZKPs, and Beyond
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) create secure enclaves within processors that execute contract logic in isolation from the broader network (ibm.com). Even node operators cannot access the underlying data during execution. Meanwhile, ZKPs enable parties to prove statements about transactions – such as compliance status – without revealing any underlying information (cioinfluence.com). This dual-layered approach ensures both operational confidentiality and regulatory auditability.
The result? Enterprises can build robust onchain compliance solutions that satisfy both internal governance standards and external regulatory audits, all without undermining client or partner privacy.
As the regulatory landscape tightens, privacy smart contracts for auditability are quickly becoming a cornerstone for enterprise blockchain adoption. The ability to generate immutable yet confidential audit trails is a game changer. Auditors can verify contract execution, check compliance with anti-money laundering protocols, and trace transaction provenance, without ever accessing the underlying sensitive data.
This is especially critical for cross-border transactions and multi-jurisdictional operations. With confidential smart contracts, organizations can demonstrate compliance in real time across different legal frameworks. The technology supports granular access controls, so only authorized entities can unlock specific pieces of information during an audit or investigation.
Real-World Impact: From Compliance Burden to Competitive Edge
Major enterprises are no longer viewing privacy as a barrier to compliance, but as a strategic asset. By adopting regulatory-compliant blockchain privacy tools, they unlock operational agility and reduce risk exposure. For example, banks leveraging Chainlink’s Blockchain Privacy Manager can execute private cross-chain swaps while maintaining strict KYC/AML standards (blog.chain.link). Healthcare networks use similar frameworks to share patient data securely with insurers and regulators, without violating HIPAA or GDPR rules.
Top Enterprise Sectors Using Onchain Compliance
-
Financial Services: Major banks and fintechs use confidential smart contracts for AML/KYC compliance, secure settlements, and privacy-preserving audits. IBM Blockchain and Chainlink Privacy Manager are leading solutions.
-
Healthcare: Hospitals and insurers leverage privacy-preserving smart contracts to secure patient data and enable regulatory reporting without exposing sensitive information. Confidential Computing for Healthcare Blockchain is a key application.
-
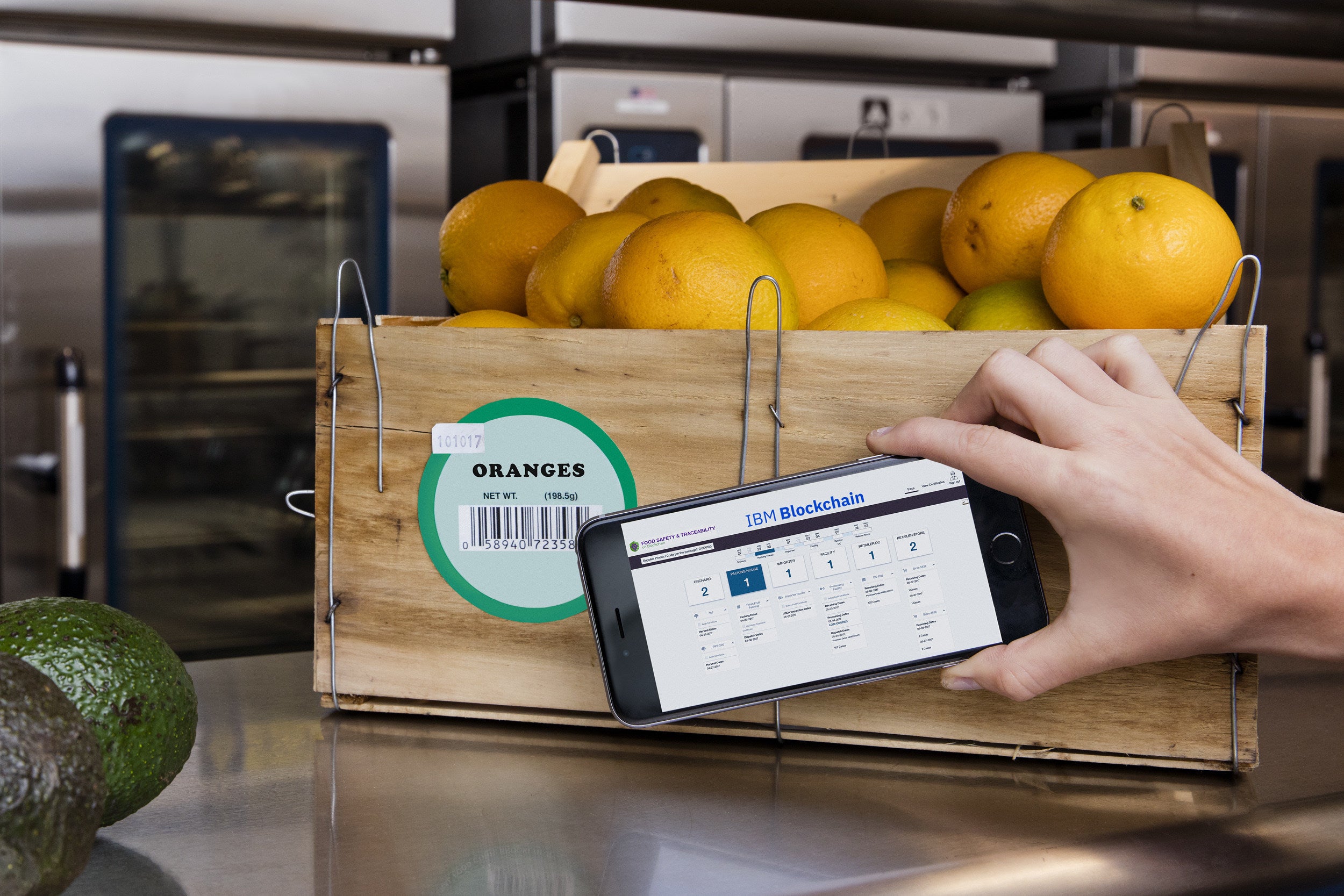

Supply Chain & Logistics: Enterprises use onchain compliance to track goods, verify provenance, and automate regulatory checks while protecting trade secrets. IBM Food Trust is a notable platform.
-

Insurance: Insurers deploy smart contracts for claims automation and fraud detection, meeting compliance standards while keeping customer data private. ConsenSys Blockchain Insurance Solutions is an industry example.
-

Public Sector & Government: Governments adopt confidential smart contracts for secure identity management, regulatory filings, and auditable public services. IBM Blockchain for Government is widely used.
The shift is also driving innovation in blockchain auditing practices. Traditional audits were slow and invasive, requiring full data dumps for verification. Now, with encrypted smart contract protocols integrating features like selective disclosure and zero-knowledge compliance proofs, auditors gain real-time assurance with minimal data exposure (arxiv.org). This not only streamlines due diligence but also builds trust between counterparties in complex supply chains or syndicated financial products.
Looking Ahead: Towards Scalable and User-Friendly Privacy
The next frontier is making these privacy-preserving technologies accessible to developers at scale. Open-source toolkits are emerging that abstract away the complexity of TEEs and ZKPs. Developers can now deploy plug-and-play modules for confidential computation and regulatory reporting, ushering in rapid prototyping cycles for new privacy-centric DeFi products or enterprise workflows.
This democratization of privacy tooling means even smaller organizations can build regulatory-compliant blockchain applications without needing a PhD in cryptography. As more jurisdictions introduce digital asset regulations mandating both transparency and confidentiality, expect confidential smart contracts to become the default standard, not the exception.
The bottom line: Confidential smart contracts empower enterprises to meet evolving compliance demands while protecting what matters most, their data and their customers’ trust.






