As privacy-centric blockchain applications mature, the need for rigorous auditing of encrypted smart contracts has never been more urgent. Unlike traditional smart contracts, encrypted variants introduce layers of complexity due to their use of advanced cryptography and confidentiality-preserving mechanisms. This article explores the top five tools and methodologies tailored specifically for auditing encrypted smart contracts, focusing on privacy assurance, vulnerability detection, and compliance with evolving privacy standards in blockchain environments.

Why Auditing Encrypted Smart Contracts Requires Specialized Approaches
Standard auditing tools can miss subtle vulnerabilities when code logic or data is intentionally obfuscated for privacy. In these cases, ensuring that confidential data remains protected while verifying contract correctness demands both technical sophistication and a nuanced understanding of cryptographic protocols. Let’s break down the curated list of tools and methodologies making waves in 2025:
Top 5 Tools & Methodologies for Auditing Encrypted Smart Contracts
-

Slither with Privacy Extension Modules: An advanced static analysis framework for Solidity smart contracts, enhanced with modules to detect privacy-specific vulnerabilities and data leakage in encrypted environments.
-

Mythril Enhanced for Encrypted Data Flows: A popular security analysis tool for Ethereum smart contracts, now featuring improved capabilities to trace and assess encrypted data flows and privacy risks.
-

Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP)-based Audit Methodologies: Cutting-edge auditing approaches leveraging ZKPs (such as zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs) to verify contract correctness and privacy without exposing sensitive information.
-
Cyfrin Aderyn for Encrypted Contract Analysis: An open-source Rust-based tool tailored for analyzing encrypted Solidity contracts, providing automated detection of privacy and security vulnerabilities.
-
Manual Code Review with Differential Fuzzing for Confidentiality: A rigorous methodology combining expert manual code review with differential fuzzing techniques to uncover subtle privacy leaks and ensure confidentiality in encrypted smart contracts.
1. Slither with Privacy Extension Modules
Slither has long been a staple for static analysis in Solidity development, but its recent privacy extension modules push it to the forefront for encrypted contract audits. These modules enable detection of vulnerabilities unique to confidential data flows, such as improper handling of encryption keys or potential leaks through metadata.
- Pros: Rapidly identifies standard and privacy-specific coding issues; integrates into CI/CD pipelines.
- Cons: May generate false positives if not properly tuned for custom encryption logic.
The ability to scan for both classic Solidity bugs and privacy leaks makes Slither with extensions an essential first step in any audit workflow.
2. Mythril Enhanced for Encrypted Data Flows
Mythril, renowned for its symbolic execution engine, now includes enhancements specifically designed to trace encrypted data flows within Ethereum bytecode. This means auditors can simulate attacks that attempt to extract or manipulate confidential information, even when the logic is obfuscated by encryption layers.
- Pros: Powerful at uncovering reentrancy issues within private functions; models complex attack scenarios on hidden data paths.
- Cons: Analysis can be computationally intensive; requires expertise to interpret nuanced results.
The enhanced Mythril tool is particularly valuable when dealing with hybrid contracts that combine public functions with sensitive internal computations.
3. Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP)-based Audit Methodologies
No discussion about privacy assurance in blockchain would be complete without zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs). ZKP-based audit methodologies allow auditors to verify that a smart contract’s private computations are correct, without revealing any underlying sensitive data. Techniques like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs are leveraged not just by developers but also by auditors seeking mathematical guarantees around confidentiality claims.
- Pros: Provides robust cryptographic guarantees; ideal for regulatory compliance where proof of correctness is required without disclosure.
- Cons: Implementing ZKP audits demands deep expertise; tooling is still evolving compared to mainstream static analyzers.
This methodology is rapidly becoming a gold standard in regulated industries where both transparency and secrecy are paramount requirements.
4. Cyfrin Aderyn for Encrypted Contract Analysis
Cyfrin Aderyn stands out as a purpose-built analyzer for encrypted smart contracts, offering a unique approach to privacy-centric auditing. Unlike generic static analyzers, Aderyn is engineered to parse and interpret Solidity Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs) with an eye for encryption-specific vulnerabilities. Its advanced logic enables the identification of subtle flaws in cryptographic integrations, such as insecure key management or side-channel leakage risks.
- Pros: Designed from the ground up for privacy contracts; open-source and extensible for new cryptographic patterns.
- Cons: Best results require familiarity with both AST structures and privacy-preserving contract design; may not support non-Solidity languages yet.
This tool’s tight integration with developer workflows makes it indispensable when reviewing codebases that rely heavily on custom encryption primitives or novel privacy protocols.
5. Manual Code Review with Differential Fuzzing for Confidentiality
No automated tool can fully replace the insight gained from expert manual review, especially when it comes to auditing encrypted smart contracts. The latest best practice merges traditional line-by-line code review with differential fuzzing: a technique that generates varied inputs to probe confidential execution paths and surface unintended information leaks.
- Pros: Uncovers nuanced bugs that evade automation; differential fuzzing exposes edge cases in encrypted logic and data handling.
- Cons: Resource-intensive; effectiveness depends on auditor experience and depth of test coverage.
This hybrid methodology is crucial for projects where absolute confidentiality is required, such as DeFi platforms handling sensitive user data or enterprise solutions subject to strict regulatory oversight.
Integrating Tools for Comprehensive Privacy Assurance
The most robust audits combine these tools and methodologies into a layered strategy. For instance, an initial pass with Slither’s privacy modules can highlight low-hanging issues, followed by Mythril’s deep dive into encrypted flows. Cyfrin Aderyn then provides context-aware analysis of encryption logic, while ZKP-based techniques mathematically validate confidential computations. Finally, manual review paired with differential fuzzing ensures that even the most sophisticated attack vectors are considered.
Steps to Prepare Encrypted Smart Contracts for Audit
-
Slither with Privacy Extension Modules: Integrate Slither into your development workflow and enable privacy-focused extension modules. This static analysis tool scans Solidity code for vulnerabilities, and with privacy modules, it highlights issues related to data exposure and improper encryption handling. Practical Step: Run Slither on your encrypted contract code, review flagged privacy risks, and refactor code to mitigate exposure before submitting for audit.
-

Mythril Enhanced for Encrypted Data Flows: Use Mythril with configurations tailored for encrypted smart contracts. Mythril simulates attack vectors and analyzes bytecode, and its enhanced settings can trace encrypted data flows to uncover reentrancy, overflows, and leakage points. Practical Step: Configure Mythril to focus on encrypted storage and transaction paths, then address any vulnerabilities it detects in your contract.
-

Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP)-based Audit Methodologies: Adopt ZKP-based auditing frameworks like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs to validate privacy guarantees without exposing sensitive data. These methodologies mathematically prove correctness and privacy compliance. Practical Step: Integrate ZKP circuits into your contract and prepare test cases that demonstrate privacy-preserving execution for auditors.
-
Cyfrin Aderyn for Encrypted Contract Analysis: Leverage Cyfrin Aderyn, an open-source Rust-based Solidity AST analyzer, to automatically review encrypted contract logic. It detects vulnerabilities and logic flaws specific to encrypted workflows. Practical Step: Run Aderyn on your contract’s source code, analyze the output for privacy and logic errors, and resolve any issues before the audit.
-
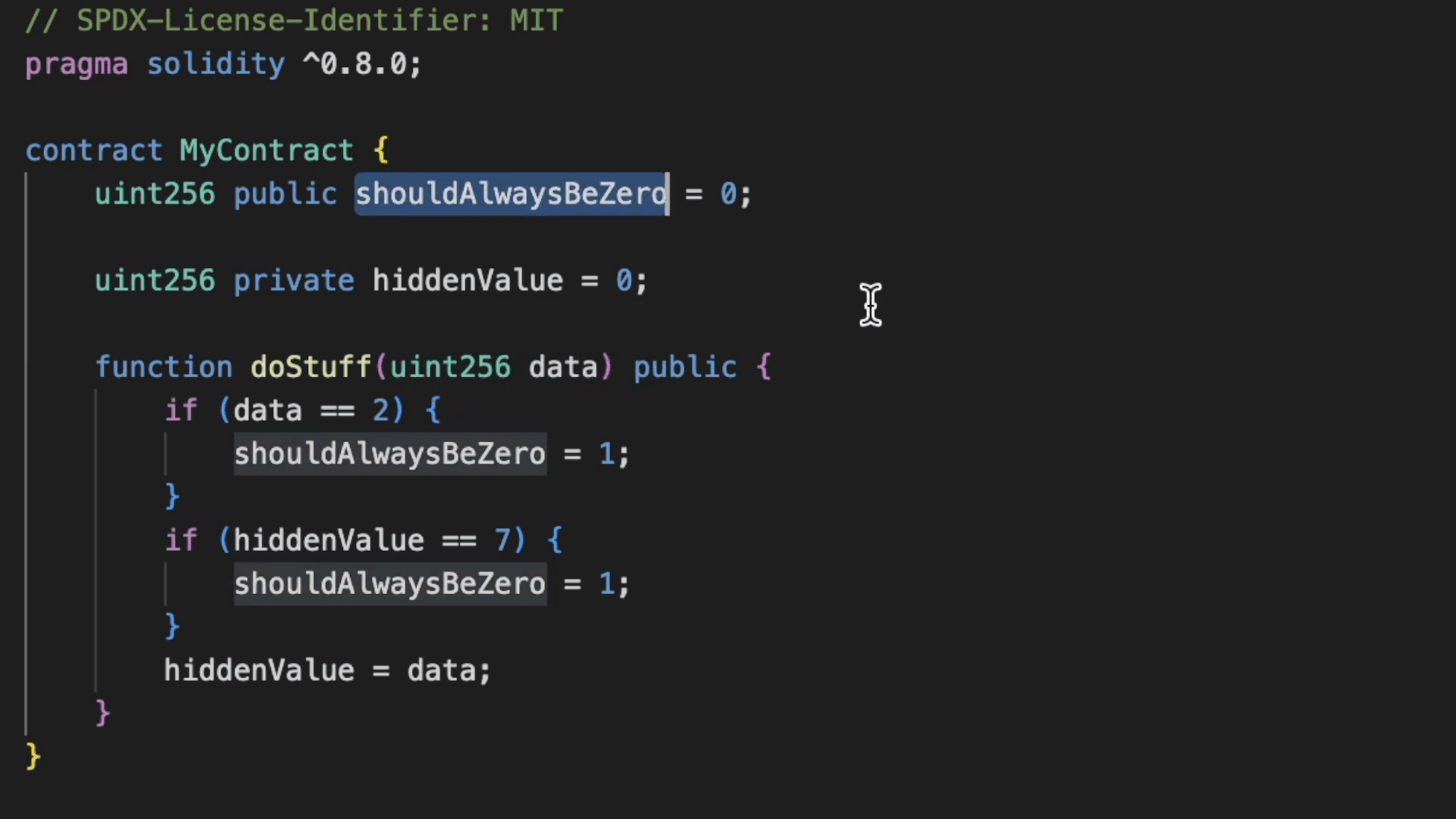
Manual Code Review with Differential Fuzzing for Confidentiality: Conduct a thorough manual review focused on privacy logic, supplemented by differential fuzzing tools that generate varied inputs to test for information leaks and confidentiality breaches. Practical Step: Document all manual review findings, run fuzzing tests targeting encrypted data paths, and patch any discovered leaks or weaknesses.
This integrated approach not only maximizes vulnerability detection but also builds confidence among users and regulators that privacy claims are substantiated by rigorous technical evidence. As blockchain adoption accelerates across sensitive sectors like finance and healthcare, such diligence is becoming table stakes, not a luxury, for any project aiming to earn market trust.






