Programmable privacy is no longer a theoretical ideal for blockchain – it is the defining feature of encrypted smart contracts in 2025. The convergence of fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), and trusted execution environments (TEEs) has transformed what smart contracts can achieve. Confidential computations are now possible directly on public blockchains, enabling complex operations on sensitive data without sacrificing transparency or regulatory compliance.

The Shift: From Static Privacy to Programmable Confidentiality
Traditional privacy solutions in blockchain were blunt instruments – either everything was public or hidden behind opaque sidechains. Today, programmable privacy smart contracts allow developers to precisely define which data stays private, who can access it, and under what conditions. This new paradigm is not just about keeping secrets; it’s about making privacy an active, customizable part of decentralized applications.
For example, Zama’s FHE-powered confidential token standard lets developers build ERC20-like tokens where balances and transfer amounts remain encrypted. Only authorized parties can decrypt transaction details, while all logic executes transparently on-chain. This granular control over data exposure is essential for compliant DeFi protocols, enterprise asset management, and even privacy-first DAOs.
Key Technologies Powering Encrypted Smart Contracts in 2025
The technical leap in 2025 comes from several complementary innovations:
- Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE): Enables computation on encrypted data without decryption. Zama’s production-ready FHE tools have made confidential governance and private token distributions possible on mainstream blockchains.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Aztec’s zkRollup for Ethereum leverages ZKPs to execute private smart contracts. Noir, a purpose-built programming language, empowers developers to craft sophisticated zero-knowledge applications with selective disclosure.
- Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): Off-chain architectures like RaceTEE use TEEs to process encrypted inputs securely and efficiently, minimizing on-chain overhead while preserving confidentiality.
- Confidential Compute Services: Chainlink’s Confidential Compute unlocks private smart contracts across any blockchain ecosystem by enabling secure off-chain computation and policy enforcement.
This multi-layered approach delivers robust privacy infrastructure for Ethereum and beyond. The result: confidential blockchain transactions are now scalable, cost-effective, and accessible to mainstream developers.
The Business Case: Compliance Without Compromise
The surge in privacy protocols for DeFi, confidential DeFi applications, and privacy-preserving wallets is not just a technical milestone – it responds directly to market demand for regulatory-compliant confidentiality. Financial institutions require auditability alongside user anonymity; enterprises want proprietary logic protected without creating legal black holes.
Innovations such as probabilistic compliance mechanisms in private wallets now enable transaction unlinkability while still supporting regulatory checks when needed. Confidential compute services facilitate the tokenization of real-world assets with built-in privacy controls – vital for sectors like healthcare or supply chain management where sensitive information must be shielded by default but accessible under lawful circumstances.
This evolution positions programmable privacy as both a shield against surveillance capitalism and an enabler of next-generation business models in Web3. For deeper technical insights into how these systems enable selective data disclosure on Ethereum, see our resource at /how-programmable-privacy-smart-contracts-enable-selective-data-disclosure-on-ethereum.
By mid-2025, the competitive edge for blockchain projects is defined by how flexibly and securely they implement encrypted smart contracts. Programmable privacy is no longer a niche feature; it’s now a baseline expectation for any protocol handling sensitive user data or institutional assets. The latest frameworks, like Paladin under the Linux Foundation, offer unified APIs for customizable privacy settings, allowing developers to programmatically balance transparency and confidentiality based on stakeholder needs.
Leading Programmable Privacy Protocols Shaping 2025
-

Zama’s Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE): Zama’s FHE technology empowers smart contracts to process encrypted data directly on public blockchains, enabling confidential governance and private token distributions without exposing sensitive information.
-
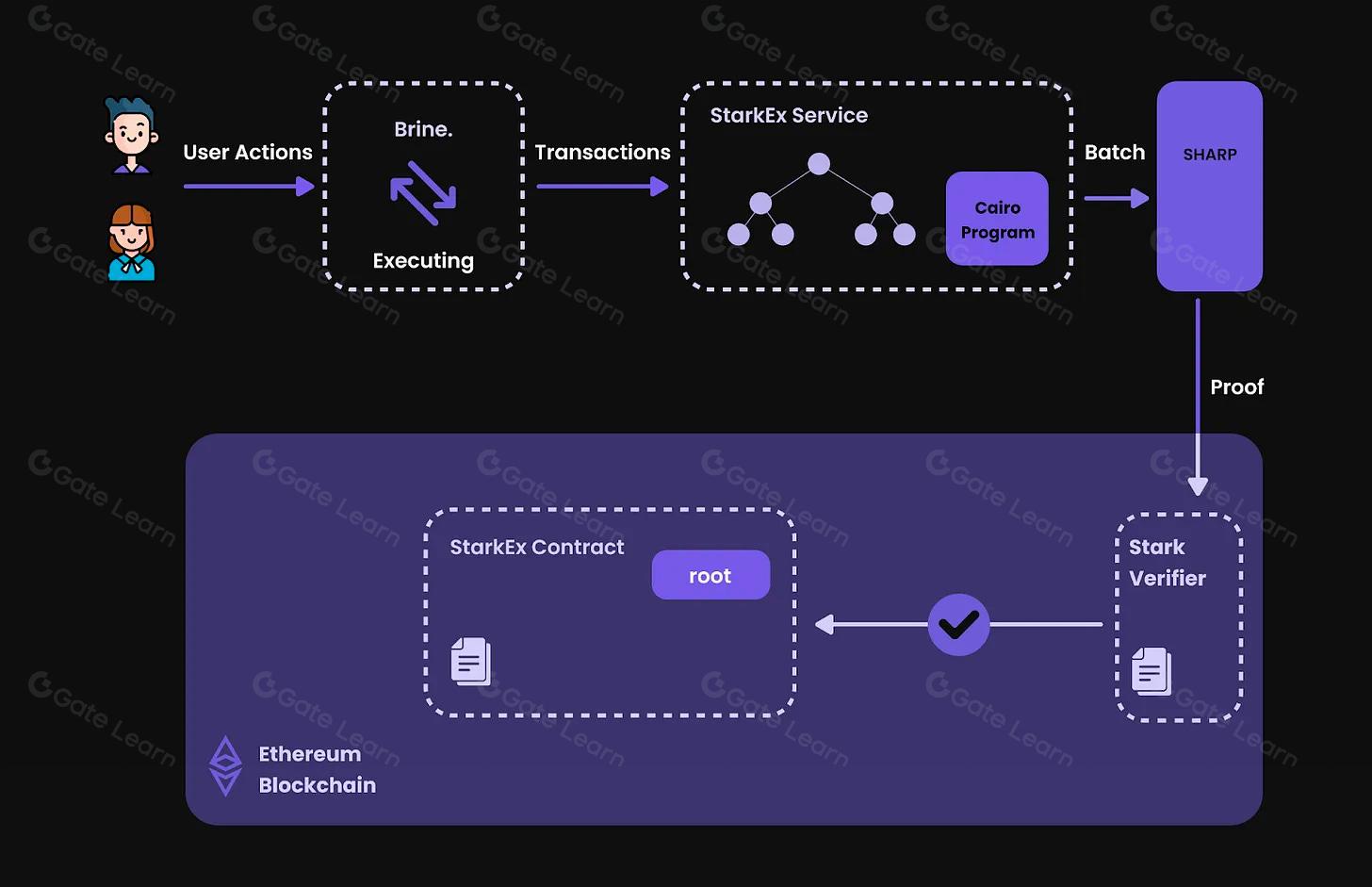
Aztec Network & Noir: Aztec leverages zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and its Noir programming language to deliver private smart contracts on Ethereum, allowing developers to finely control data disclosure in DeFi and beyond.
-

OpenZeppelin Confidential Token Standard: In partnership with Zama, OpenZeppelin has introduced a confidential token interface similar to ERC20, but with encrypted balances and transaction values, ensuring user privacy in dApps.
-
Chainlink Confidential Compute: Chainlink’s Confidential Compute service enables private smart contracts and confidential data processing across blockchains, supporting privacy-preserving tokenization and compliance automation.
-
RaceTEE Trusted Execution Environments: RaceTEE utilizes trusted execution environments (TEEs) for secure off-chain computation on encrypted data, supporting confidential inter-contract interactions and advanced privacy features.
-

Privacy-Preserving Smart Wallets: Next-generation smart wallets now feature probabilistic compliance and encrypted contact management, enabling private, unlinkable transactions while meeting regulatory requirements.
Consider the impact on decentralized finance: privacy infrastructure on Ethereum now supports confidential lending pools where loan amounts and collateral can be verified by smart contracts without revealing specifics to the public. This not only protects user interests but also attracts institutional capital that was previously sidelined due to compliance risks. At the same time, privacy-preserving governance enables DAOs to conduct votes where results are auditable but individual choices remain private, crucial for both regulatory alignment and community trust.
On-chain privacy is also being extended to off-chain data flows through confidential compute oracles. Chainlink’s Confidential Compute service, for instance, orchestrates secure data feeds from traditional systems into smart contracts without exposing underlying business logic or trade secrets. These advances are accelerating tokenization of real-world assets, think healthcare records or supply chain provenance, where programmable privacy ensures only authorized actors can decrypt sensitive fields while maintaining full audit trails for compliance.
Challenges and amp; Opportunities: What’s Next for Programmable Privacy?
Despite these breakthroughs, implementing privacy protocols for DeFi at scale still presents hurdles. FHE and ZKP computations remain resource-intensive compared to traditional cryptography. However, hybrid models combining TEEs with efficient zero-knowledge circuits are rapidly closing this gap, making confidential DeFi applications more practical than ever before.
The next frontier is interoperability: enabling seamless private transactions across multiple blockchains without sacrificing confidentiality or composability. Cross-chain bridges equipped with programmable privacy logic are in early deployment phases, promising a future where users can move assets and data between ecosystems with full control over what is revealed at each step.
This evolution isn’t just technical, it’s cultural. Users increasingly expect granular control over their digital footprint, while regulators demand provable compliance without mass surveillance. Programmable privacy smart contracts uniquely satisfy both imperatives by embedding policy logic directly into code, ensuring that privacy is not an afterthought but a programmable guarantee.
The paradigm shift is clear: as programmable privacy matures, it will underpin not just financial applications but any domain requiring selective confidentiality, identity management, voting systems, intellectual property rights, and more. For those building in this space today, strategic investment in robust privacy infrastructure will define tomorrow’s market leaders.






