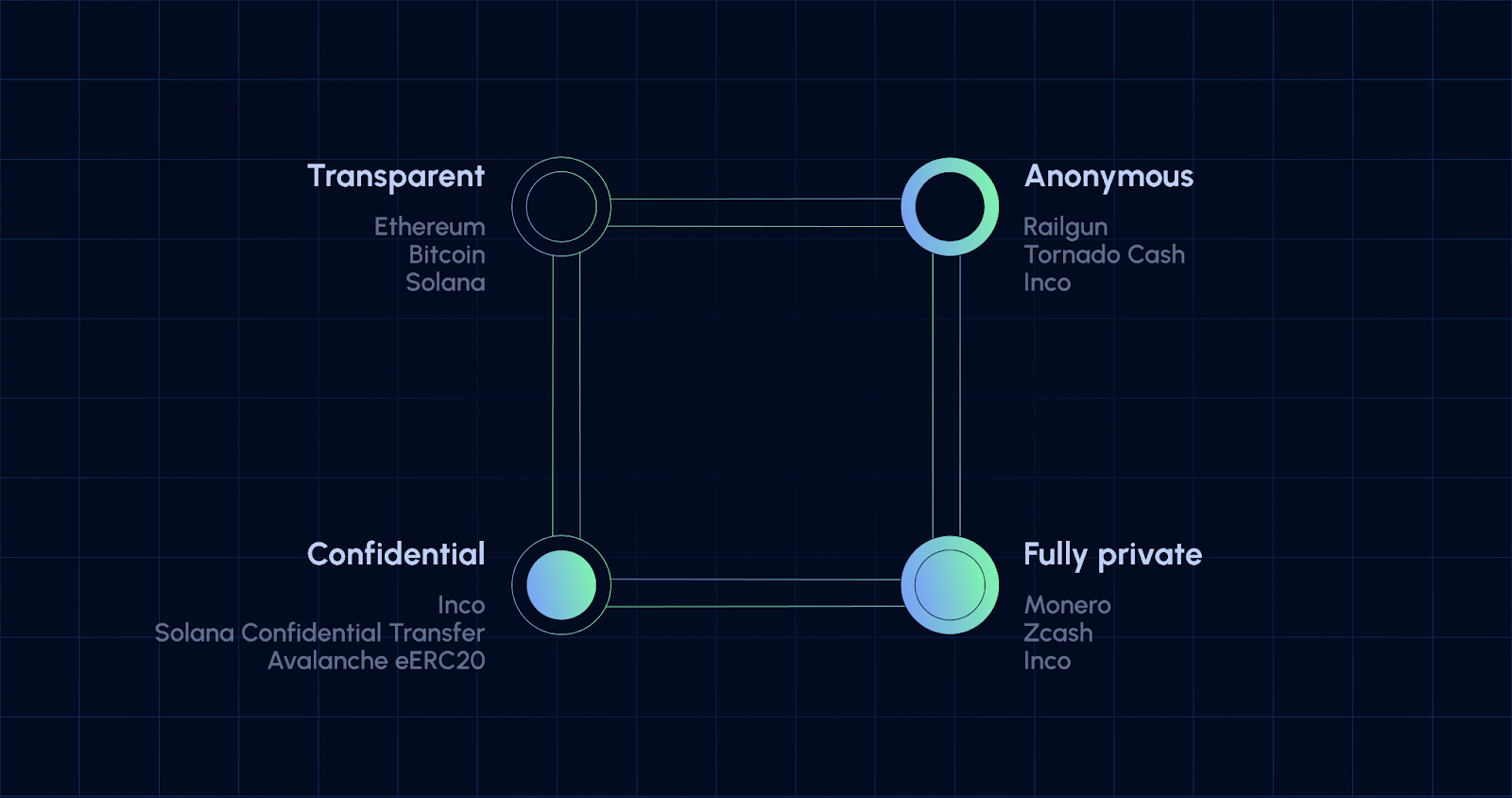
On Ethereum, every smart contract interaction is visible on-chain. This radical transparency powers DeFi, but it comes at a cost: sensitive trading strategies, balances, and user identities are exposed to anyone with a block explorer. As private DeFi transactions become a necessity for institutions and privacy-conscious users, encrypted smart contracts are the next leap in blockchain security.
Why Privacy Matters in DeFi at $3,588.22 ETH
Ethereum’s current price of $3,588.22 reflects ongoing demand for programmable money and decentralized applications. Yet, as more capital flows into DeFi protocols, adversaries have greater incentive to exploit transparency for front-running or surveillance. The need for encrypted smart contracts isn’t theoretical – it’s a market imperative.
Private DeFi transactions protect not just whales and trading firms, but also everyday users who want to keep their balances confidential or shield their financial history from public scrutiny. This shift is accelerating as new cryptographic primitives mature and regulatory pressure mounts on open ledgers.
The Core Technologies Powering Confidential Smart Contracts
The past two years have seen breakthroughs in privacy-preserving computation on Ethereum:
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Protocols like Zether use ZKPs to hide transaction amounts and participant identities while still allowing public validation of contract logic. This means you can prove a trade happened without revealing the details.
- Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE): FHE allows computations directly on encrypted data. Frameworks like smartFHE bring this capability to Ethereum-like blockchains, enabling private smart contracts that never expose raw inputs or outputs.
- Layer-2 Privacy Solutions: Aztec Network leverages zk-Rollups so that users can interact privately with DeFi protocols at scale – encrypting transaction data while maintaining composability with the broader Ethereum ecosystem.
- Confidential Token Standards: Collaborations between Zama and OpenZeppelin have produced confidential token interfaces that support encrypted balances and transfers without sacrificing compatibility or auditability.
- Additive Privacy Layers: Silent Protocol’s plug-and-play privacy layers let existing dApps offer anonymous interactions with minimal code changes or user friction.
Navigating Implementation: Key Considerations for Developers
Pushing privacy into Ethereum’s DNA is not trivial. Developers must weigh several factors:
- Performance Overheads: Encrypted computations (especially FHE) can slow down execution and increase gas costs compared to plain Solidity contracts.
- Regulatory Compliance: While privacy is essential, compliance with AML/KYC rules remains critical for institutional adoption. Encrypted contracts must enable selective disclosure when required by law.
- Ecosystem Interoperability: The best privacy solutions integrate seamlessly with existing wallets, dApps, and infrastructure – ensuring users don’t sacrifice usability or composability for confidentiality.
If you’re ready to dive deeper into implementation patterns for encrypted smart contracts in DeFi, see our detailed guide: How to Implement Encrypted Smart Contracts for Confidential DeFi Transactions.
Building on these innovations, the privacy landscape on Ethereum is evolving rapidly. As of late 2025, with ETH steady at $3,588.22, projects are racing to deliver seamless privacy without compromising Ethereum’s hallmark composability. Let’s break down what this means for developers, enterprises, and users navigating the next era of confidential DeFi.
Practical Steps to Integrate Encrypted Smart Contracts
Implementing encrypted smart contracts on Ethereum involves a blend of cryptography, protocol selection, and user experience design. Here’s how teams are approaching it:
Top Practices for Encrypted Smart Contracts in DeFi
-

Leverage Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) to ensure transaction privacy. Protocols like Zether enable confidential payments on Ethereum by hiding transaction amounts and participants.
-
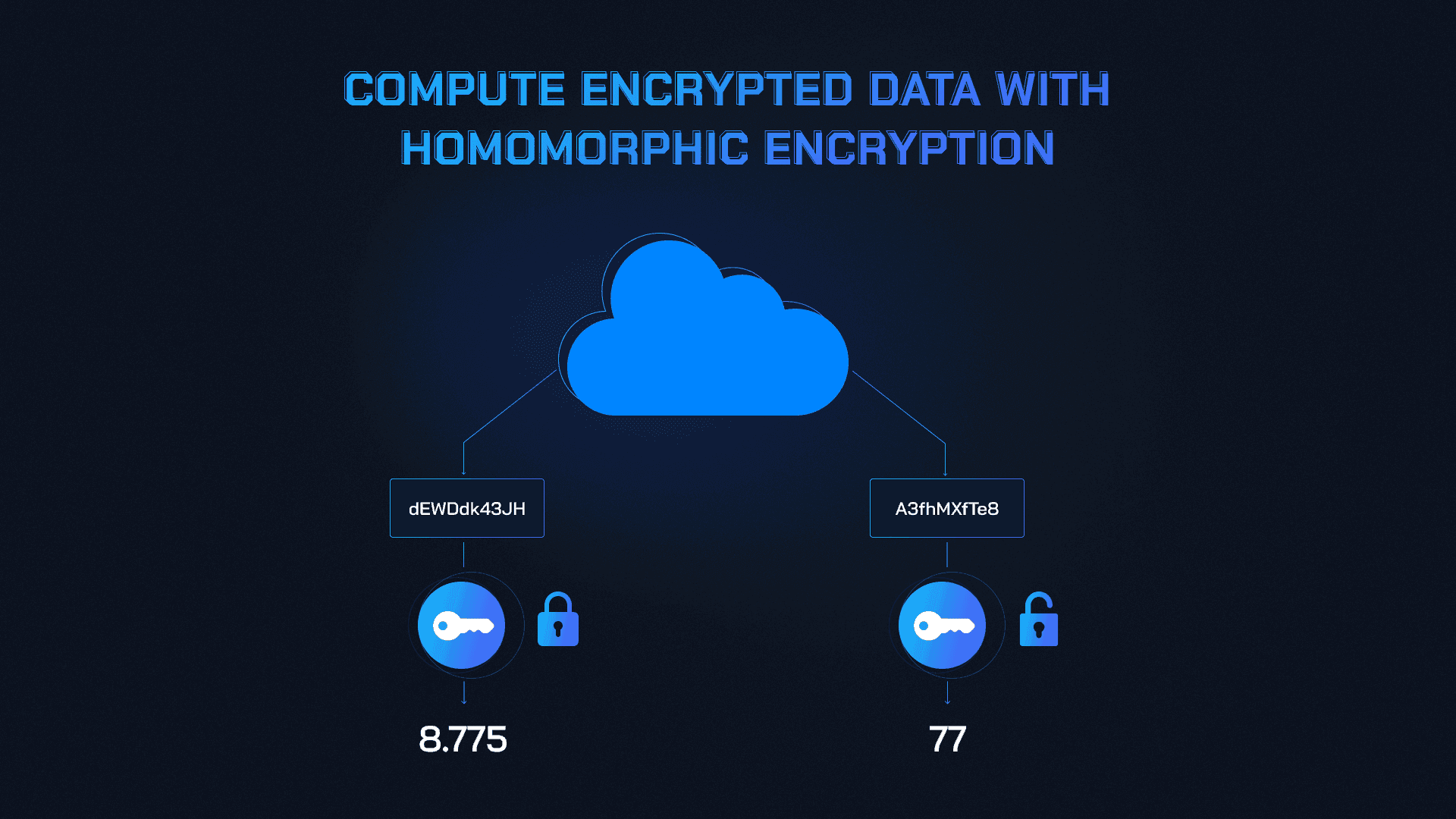
Adopt Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) frameworks such as smartFHE for private computations. FHE allows smart contracts to process encrypted data without decryption, maintaining confidentiality end-to-end.
-

Utilize Layer-2 Privacy Solutions like Aztec Network to scale and secure DeFi. Aztec uses zk-Rollups to encrypt transaction data while validating it with zero-knowledge proofs.
-

Implement Confidential Token Standards with projects like Zama and OpenZeppelin. Their confidential token interfaces allow for encrypted balances and private transfers on Ethereum.
-
Integrate Privacy-Preserving Protocols such as Silent Protocol for anonymous DeFi interactions. Frameworks like EZEE enable users to engage with smart contracts while keeping transaction details confidential.
1. Choose Your Privacy Layer: Decide between native L1 solutions (e. g. , ZKPs directly in Solidity), Layer-2 rollups like Aztec for scalable privacy, or hybrid approaches using FHE frameworks such as smartFHE.
2. Leverage Confidential Token Standards: Adopt confidential ERC interfaces so users can transact privately while still interacting with existing DeFi protocols and wallets.
3. Optimize for Gas and UX: Use off-chain computation where possible to minimize gas costs associated with heavy cryptography. Prioritize wallet integrations that abstract away complexity for end-users.
4. Enable Selective Disclosure: Build mechanisms allowing users to share proofs or partial transaction data to meet compliance checks without exposing their full activity on-chain.
What Does Private DeFi Actually Unlock?
The arrival of confidential smart contracts isn’t just a technical upgrade, it’s a paradigm shift for blockchain utility:
- Institutional Onboarding: Hedge funds and trading desks can execute strategies without leaking alpha or risking MEV attacks.
- User Protection: Retail traders gain control over their financial privacy in an age where data scraping is rampant.
- Diverse Use Cases: From private lending pools to confidential auctions and voting systems, encrypted contracts expand the design space far beyond simple swaps or loans.
Challenges on the Road to Default Privacy
No breakthrough comes without friction. The most common hurdles today include:
- Evolving Standards: Privacy protocols are iterating fast, developers must track updates from Zama, OpenZeppelin, Aztec, and others to avoid building atop legacy tech.
- User Education: Many users still equate blockchain with transparency; onboarding them into private DeFi requires clear messaging about benefits and trade-offs.
- Ecosystem Fragmentation: With multiple competing privacy stacks, cross-dApp composability can suffer if standards don’t converge quickly enough.
The Future: Towards Default-Private Ethereum
If current momentum holds, we’re approaching an inflection point where EVM-compatible privacy becomes the norm rather than the exception. As regulatory clarity improves and cryptographic primitives become more efficient, expect major DeFi protocols to offer private modes by default, potentially reshaping how value flows through open finance at every price level above $3,588.22 ETH.
The bottom line: encrypted smart contracts are not just a technical curiosity, they’re foundational for Ethereum’s next growth phase as a secure platform for programmable money and sensitive financial logic. If you want step-by-step implementation details or code samples tailored to your stack, explore our comprehensive guide: How to Implement Encrypted Smart Contracts for Confidential DeFi Transactions.






